Image Generation using Generative Models
Access the project in: here
Blog: Enhancing Image Generation with Advanced Models
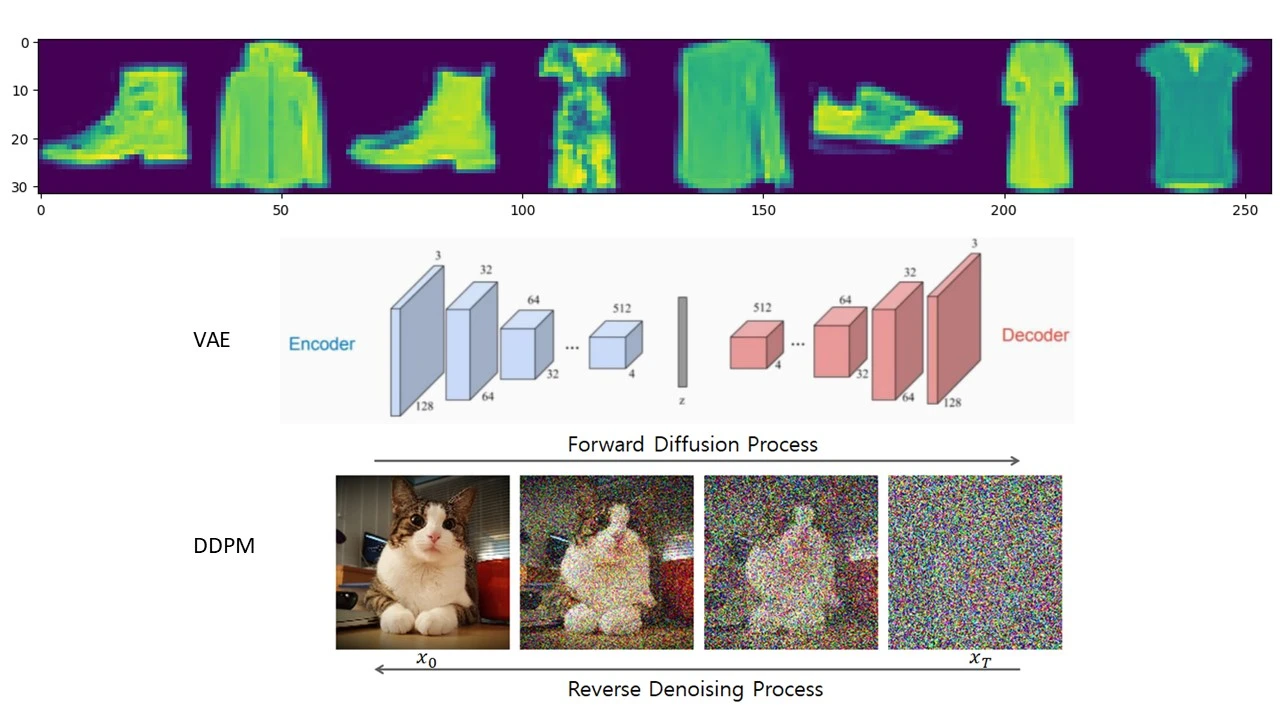
In this blog, we’re diving deep into the world of advanced models and their applications, using the FashionMNIST dataset as our playground. FashionMNIST consists of a training set of 60,000 examples and a test set of 10,000 samples. Each sample is a 28x28 grayscale image associated with a label from 10 classes. We’ll use the training split in this notebook. You can also use tools like plot_samples to visualize a sequence of images, such as iteratively denoised images by DDPM.
Variational Autoencoder (VAE)
VAE is a generative model that consists of an encoder and a decoder network. The encoder maps the input data into a latent space represented by probability distributions, while the decoder generates output data from samples of the latent space. VAE is trained using a variational inference approach with the objective to maximize the evidence lower bound (ELBO) of the data’s log-likelihood. The ELBO includes two main components: the reconstruction loss, which measures how well the decoder can reconstruct the input data, and the KL divergence between the prior (Gaussian) and posterior distributions over the latent space. The encoder learns the mean and variance of this distribution, and the reparameterization trick is used for sampling from the encoder.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN)
GAN’s architecture involves a Discriminator and a Generator. The Discriminator determines whether an input image is real or generated by the Generator. The Generator, on the other hand, creates fake images from random noise such that the Discriminator cannot distinguish them from real images. This adversarial dynamic results in the standard min-max loss for GANs, where the Generator attempts to minimize the loss while the Discriminator aims to maximize it. Each network optimizes its parameters alternately, with the Discriminator focusing on distinguishing real from fake images, and the Generator trying to fool the Discriminator.
Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM)
DDPMs generate images by progressively denoising a completely random pattern in a step-by-step process. The model learns diffusion steps to describe noise evolution over time and employs a neural network as a denoising function at each step. By iteratively removing noise, DDPMs can generate images from the training distribution. The training and sampling processes in DDPM involve complex procedures that are detailed in the original DDPM paper.
Training and Implementation
For our experiments, we’ll use the FashionMNIST dataset and implement various models, such as VAE and GAN, to explore their effectiveness in image generation tasks. Additionally, we’ll look into the use of DDPMs for generating high-quality images from noisy patterns.
Variational Autoencoder
The VAE consists of an encoder and a decoder. The encoder compresses the input images into a latent representation, while the decoder reconstructs the images from this latent space. The VAE model is trained by minimizing the reconstruction loss and the KL divergence between the latent space and the prior distribution.
Generative Adversarial Network
The GAN model includes a Generator that produces images and a Discriminator that evaluates them. The training process involves optimizing the min-max loss function, where the Generator tries to create realistic images and the Discriminator strives to correctly classify real and fake images.
Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models
DDPMs work by iteratively denoising a random input. The model learns a set of diffusion steps that describe the noise process and a denoising function to reverse it. Training DDPMs involves optimizing the denoising function to accurately reconstruct images at each step.
Conclusion
These advanced models offer powerful tools for image generation tasks. By leveraging the FashionMNIST dataset, we can explore the capabilities of VAE, GAN, and DDPM, each providing unique approaches to generating high-quality images. Our journey through these models will showcase their strengths, implementation details, and potential applications in various fields.